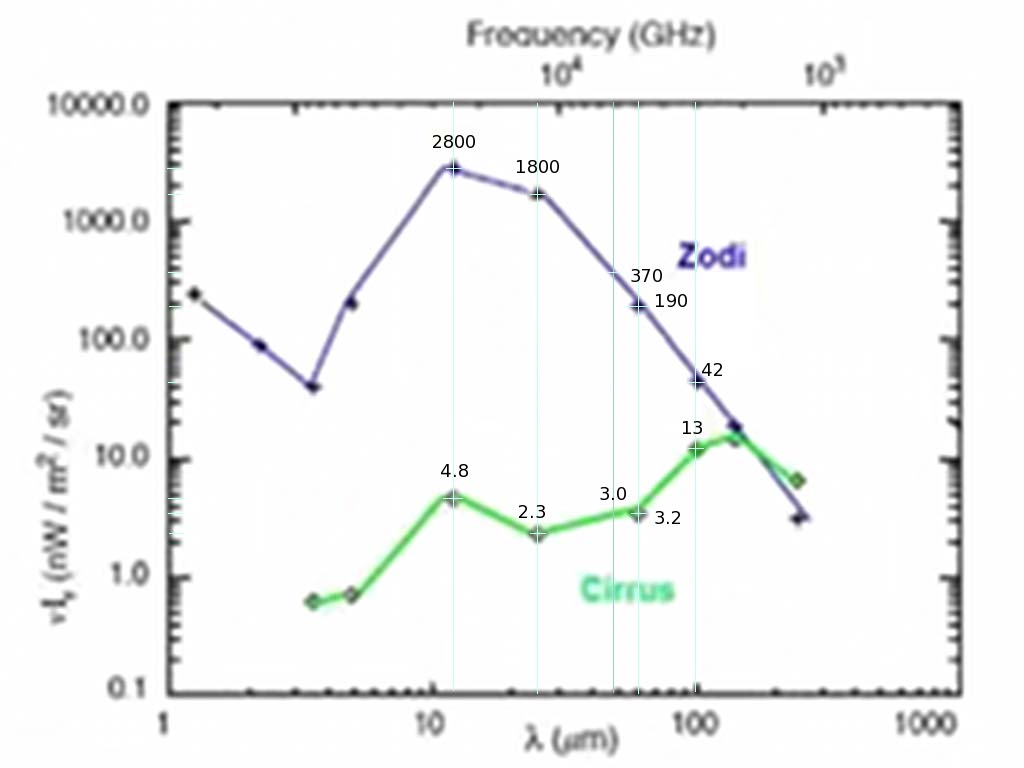
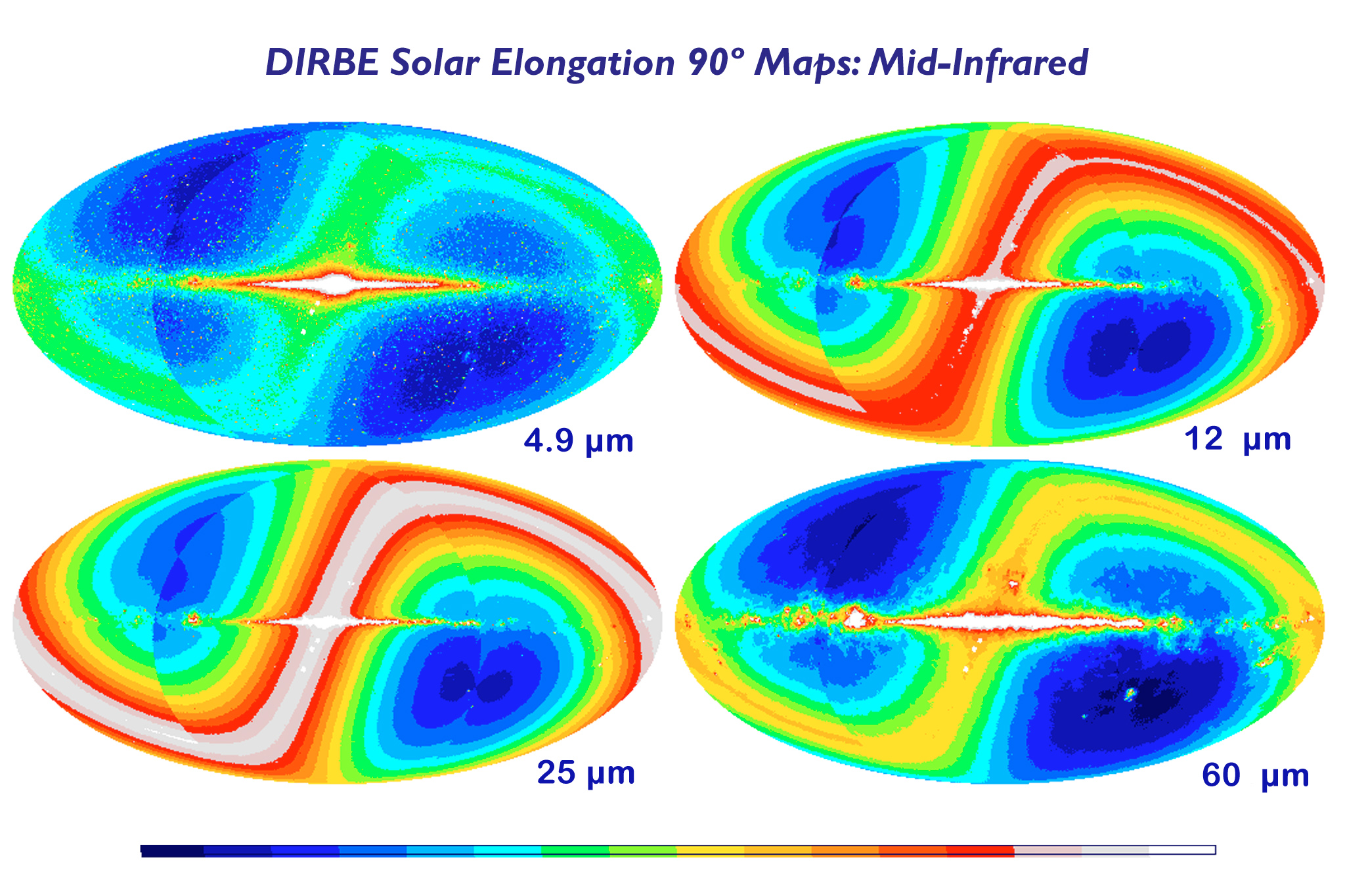
Galactic Cirrus and Zodiacal Light
60K 50AU Dyson shell
\Large B(\lambda) = \LARGE { { 2 h c } \over { \lambda^3 \left( e^{ h c / \lambda k T } - 1 \right) } } = { { 4e19 ~ Jy / sr ~ {\mu}m^3 } \over { \lambda^3 \left( e^{ 240 {\mu} m / \lambda } - 1 \right) } }
This is for an infinite resolution imager - at large distances, the power is the image angular area divided by the pixel angular area. This scales the intensity way down for distant Dyson shells. If the ratio of shell intensity to background is F , the pixel size in arcseconds is px , the shell radius in AU is r , and the distance in parsecs is R , then the angular size A is:
A ~ = ~ \pi ( r / R )^2
F ~ = ~ px^2 / A = ( px ~ R / r ) ^2 / \pi
R ~ = ~ ( 50" / px ) \sqrt{ \pi F }
Detectability
px is 90" (90 arcseconds) for IRAS, 12" for WISE, and .11" for JWST. It is 2.3" for Spitzer MIPS (Multiband Imaging Photometer for Spitzer) 24 μm (128x128 pixels) and 9.4" for Spitzer 70 μm (16x32 pixels).
R ~=~ 0.96 \sqrt{ F } for IRAS, 7.2 \sqrt{ F } for WISE, and 790 \sqrt{ F } for JWST. Of those three, only IRAS has sensors for wavelengths longer than 25 μm. R ~=~ 38 \sqrt{ F } for 24 μm Spitzer and 9.2 \sqrt{ F } for 70 μm Spitzer.
Disk
Assume 3 pixels wide for identification of a disk. IRAS can "see" a 270" disk ( 100/270 = 0.37 pc away - nothing expected), WISE can see a disk (100/12 = 8.3 pc away ), etc:
|
Pixel |
Image |
IRAS |
90" |
0.37 |
WISE |
12" |
2.8 |
Spitzer 24 μm |
2.3" |
14.5 |
JWST 25 μm |
0.11" |
300 |
 from http://lambda.gsfc.nasa.gov/product/cobe/cobe_image_table.cfm
from http://lambda.gsfc.nasa.gov/product/cobe/cobe_image_table.cfm
The graphs at the NASA site are not scaled, but they resemble logarithmic-scaled graphs in Kelsall, 1998, Figure 2. Units MJy/sr.
Color |
Blue |
Blue |
Blue |
Blue |
Cyan |
Cyan |
Gren |
Gren |
Yelw |
Yelw |
Orng |
Orng |
Red |
Red |
Gray |
Gray |
Whit |
4.9 μm |
0.10 |
0.14 |
0.19 |
0.26 |
0.35 |
0.49 |
0.67 |
0.92 |
1.26 |
1.72 |
2.37 |
3.25 |
4.46 |
6.12 |
8.39 |
11.5 |
15.8 |
12 μm |
1.58 |
2.02 |
2.58 |
3.29 |
4.21 |
5.37 |
6.86 |
8.77 |
11.2 |
14.3 |
18.3 |
23.3 |
29.8 |
38.1 |
48.7 |
62.2 |
79.4 |
25 μm |
3.98 |
4.80 |
5.79 |
6.98 |
8.41 |
10.1 |
12.2 |
14.7 |
17.8 |
21.4 |
25.8 |
31.2 |
37.6 |
45.3 |
54.6 |
65.9 |
79.4 |
60 μm |
1.00 |
1.31 |
1.73 |
2.27 |
2.99 |
3.92 |
5.16 |
6.78 |
8.91 |
11.7 |
15.4 |
20.2 |
26.6 |
35.0 |
46.0 |
60.4 |
79.4 |
The zodiac is highly inclined compared to the galaxy, but these plots show it intersecting near galactic center. This is fortunate if true - we are unlikely to distinguish a Dyson shell where the background is very dense (too confusing) or very thin (radially outwards, fewer candidates) - this puts two problem areas in the same place.
frequency = 299792 GHz-μm/λ
- Ellis: Z zodiacal, C cirrus
- B 60K 100 AU 1-sun Dyson, full pixel
Band(um) |
12μm |
25μm |
60μm |
70 μm |
100μm |
|
frequency |
25 THz |
12 THz |
5 THz |
4.3 THz |
3 THz |
|
Z nW/m2-sr |
2800 |
1800 |
190 |
130 |
42 |
|
Z Jy-sr |
1.12e7 |
1.5e7 |
3.8e6 |
3.0e6 |
1.4e6 |
|
C nW/m2-sr |
4.8 |
2.3 |
3.2 |
4.5 |
13 |
|
C Jy-sr |
1.9e4 |
1.9e4 |
6.4e4 |
1.1e5 |
4.3e5 |
|
B Jy-sr |
4.8e7 |
1.7e11 |
3.5e12 |
3.9e12 |
4.0e12 |
|
B/(C+Z) |
4.3 |
1.1e4 |
9.1e5 |
1.3e6 |
2.2e6 |
we may ignore zodiacal measurements |
F=B/C |
2.5e3 |
8.9e6 |
5.5e7 |
3.5e7 |
9.3e6 |
assume measurements in galactic plane |
R IRAS pc |
48 |
2900 |
7100 |
-- |
2900 |
|
R WISE pc |
360 |
21000 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
|
R Spitzer pc |
-- |
110000 |
-- |
54000 |
-- |
|
R JWST pc |
40000 |
2400000 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
Question: In the very short wavelengths, does the presence of a shell block luminosity in a detectable way - a "round hole" in a uniform nebula?