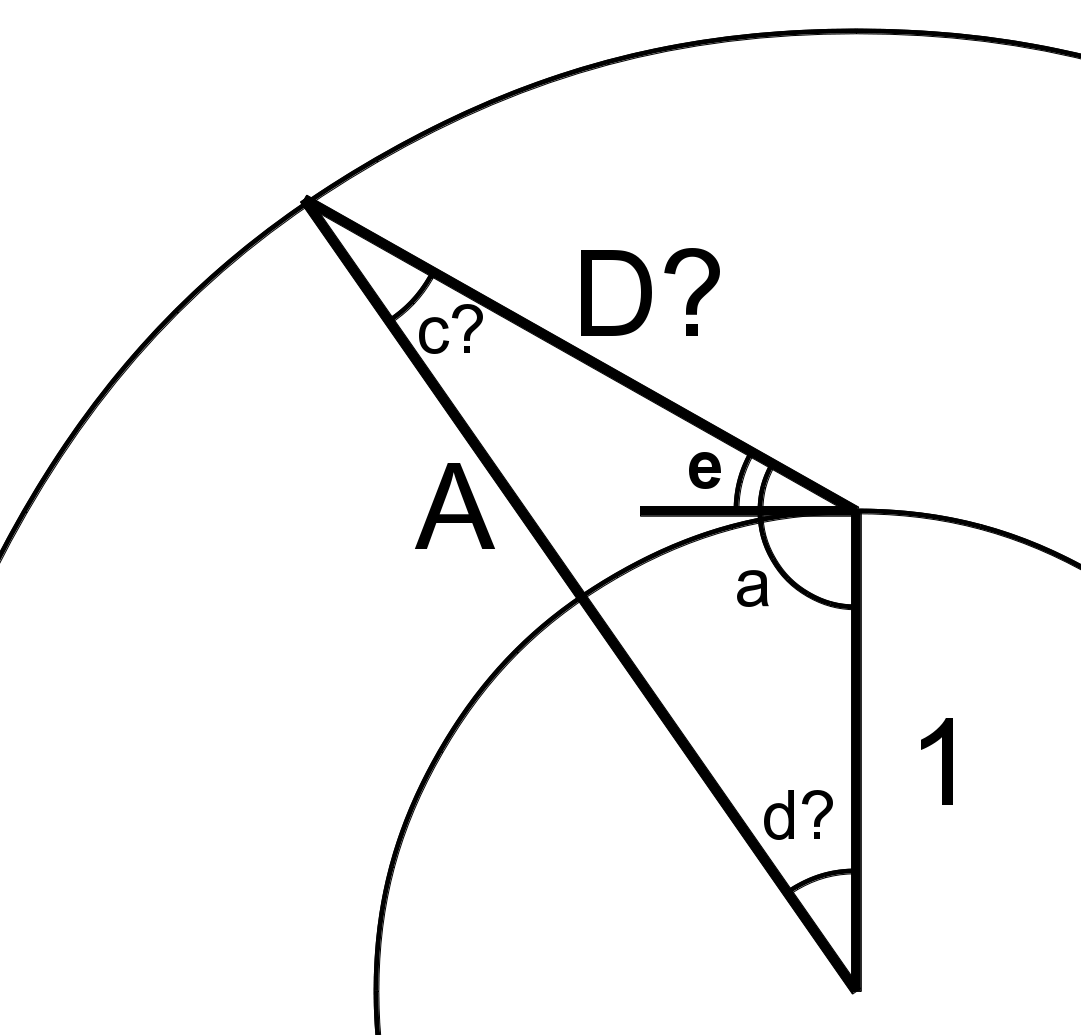
Satellite Distance
Thinsat arrays will not always be directly above the ground antenna, but will be at an elevation angle e above the horizon. If the array orbits at a radius A \bullet R_E , what is the distance D \bullet R_E between the array and the ground antenna? Note that D = 1 when elevation angle e is \pi / 2 or 90°. |
|
The sin law states that:
{ { sin( d ) } \over D } = { { sin( a ) } \over A } = { { sin( c ) } \over 1 }
sin( a ) = sin( e + { \pi \over 2 } ) = \cos( e )
sin( c ) = { { sin( a ) } \over A } = { { cos( e ) } \over A }
cos( c ) = \sqrt{ 1 - \left( { cos( e )^2 } \over A \right)^2 }
The sum of the corners of a triangle is \pi , so
\pi = a + c + d = e + { \pi \over 2 } + c + d \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; { \pi \over 2 } = e + c + d \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; d = { \pi \over 2 } - ( e + c )
sin( d ) = sin( { \pi \over 2 } - ( e + c ) ) \;\;\; = cos( e + c ) \;\;\; = cos( e ) cos( c ) - sin( e ) sin( c )
D = sin( d ) / sin( c ) \;\;\; = cos( e ) cos( c ) / ( cos( e ) / A ) - sin( e ) sin( c ) / sin( c ) \;\;\; = A cos( c ) - sin( e )
D = A \sqrt{ 1 - \left( { cos( e )^2 } \over A \right)^2 } - sin( e ) \;\;\; = \sqrt{ A^2 - cos( e )^2 } - sin( e )
D = \sqrt{ ( A^2 - 1 ) + sin( e )^2 } - sin( e ) |